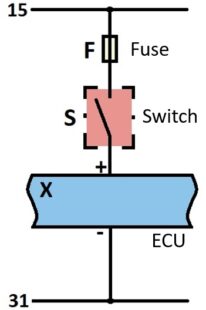
Mode sensor test
All mode sensors on vehicles have the same purpose and the same principle of operation. They convert the current mode through buttons or switches into an electrical signal and send it to the electronic control unit (ECU) for further processing. Button/switch activation can be done mechanically, pneumatically, hydraulically, thermally, or electrically.
Possible malfunctions and the test method are the same for all mode sensors. Malfunctions that can occur on the mode sensor are: faulty button/switch, interruption of the sensor’s power supply (plus or minus depending on the type of power supply), interruption of the power supply from the ECU (plus or minus), or open-circuit between the sensor and the ECU or the power supply.
When the mode sensor is suspected to be defective, we first determine the vehicle’s malfunction through system diagnostics. Then we get information about the mode sensor from the information system (installation position, wiring diagram, actual values, recommended test procedure, etc.).
The test procedure begins with disconnection by removing the socket from the mode sensor. With the given contact on the starting switch of the vehicle, we measure the power supply at the removed socket. In the event of a power failure in the outlet, detailed testing continues to determine the cause of the malfunction. It is checked whether there has been an interruption of the power supply from the network or the ECU. Then it is checked that the connection line is not the cause of the power interruption.
If there is power on the socket, we proceed to check the correctness of the buttons/switches.
When the malfunction is detected and eliminated, a final check of the correctness of the mode sensor on the vehicle is performed through diagnostics.
The described test procedure applies to all mode sensors on vehicles.
To test the mode sensor, follow these steps: