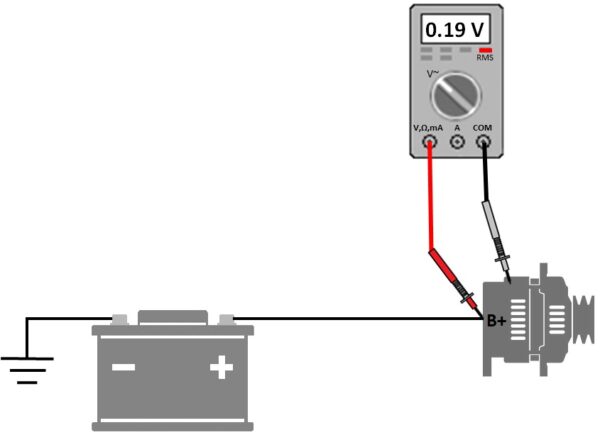
AC ripple voltage test
AC ripple voltage test at the alternator output is a procedure for determining the presence of an alternating component in the direct voltage. Electronic components are sensitive if an AC component is coming through the power supply, and it may break down. Testing is done by oscilloscope recording of the output signal. If you don’t have an oscilloscope or want an even faster test for the presence of an AC component in the power supply, you can measure with a multimeter.
Connect the plus measuring pipette of the multimeter to the plus output of the alternator (B+) and the minus pipette to the housing (ground). Set a small value AC voltage measurement, and it preferably turns on the RMS (root mean square) option. Measurement is performed under load and at 2000-2500 rpm. While the engine is running, the headlights and additional devices turn on to load the alternator. Any measured AC voltage greater than 0.25 V means that there is an AC component and that the alternator is faulty, that is, some diode is defective.