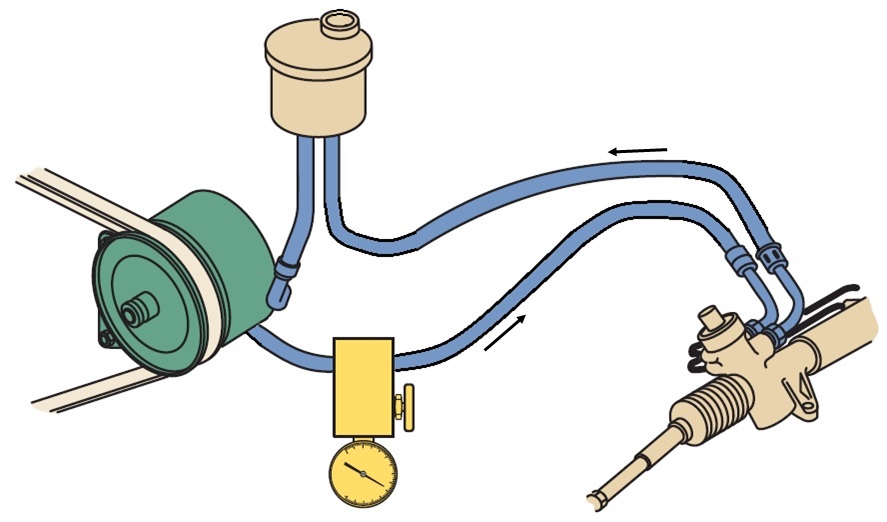
Power steering pressure test
A pressure test of the power steering system is performed when the customer complains of difficult steering or when there are repeated hose failures. Newer models of vehicles with a hydraulic steering system contain a pressure sensor and through diagnostics, the pressure of the steering fluid in the steering system can be checked and monitored. In vehicles that do not have a pressure sensor, a manometer is connected to the hydraulic part of the steering to measure the pressure of the steering fluid.
A suitable adapter with a valve and pressure gauge is installed on the drain line of the servo system. The working pressure, maximum pressure, and flow rate of the steering fluid are tested. The test checks the operation of the power steering pump, pressure regulator, control valve, pressure piston, and hose.
Power steering pressure tester
Connecting the pressure gauge is done with the engine off. Raise the vehicle so that the front wheels are off the ground. A container for collecting steering fluid is placed under the steering pump. Then the drain pressure hose is separated from the steering pump. Be careful if the engine is hot because then the power steering fluid is also hot and can be under pressure. It is recommended to wait for a little so that the fluid cools down and the pressure in the hydraulic steering system drops.
An adapter with a pressure gauge is connected to the place of the separated hose. Add steering fluid, and start the engine for 2 minutes to bleed from the steering system. That’s how we prepared for testing.
Start the engine again steering wheel is in the neutral position (wheels in the straight-ahead position). The engine is idle, and the pressure is read from the manometer. When the pressure value is higher than required, check the power steering hoses for restrictions.
Power steering pressure test
Then the valve on the manometer adapter is closed briefly two or three times (no longer than 5 seconds), and the highest measured pressure of the steering fluid is recorded. If the pressure is lower than the specification, the steering fluid supply is low, and the steering pump needs to be checked.
Finally, with the valve open and the engine running, the steering wheel all the way and read the pressure. In the same way, measure the pressure on the second full turn of the steering wheel. The measured pressures on one and the other end stop of the steering wheel should be maximum and equal. If there is maximum pressure on one and lower pressure on the other, replace the control box on the steering rack. If the measured pressures are below the maximum value, replace the servo pump with a new one.
When the pressure drops and the steering fluid cools, remove the manometer adapter and connect the pressure hose to the steering pump. Fluid is added, and the bleed from the steering system. Discarded steering fluid is properly disposed of by regulations for the disposal and storage of hazardous liquids.
If the vehicle has a pressure sensor in the power steering system, the pressure test procedure is the same, except that the pressure gauge is not installed. The pressure state from the sensor is monitored via a diagnostic tool.
To power steering pressure test, follow these steps: